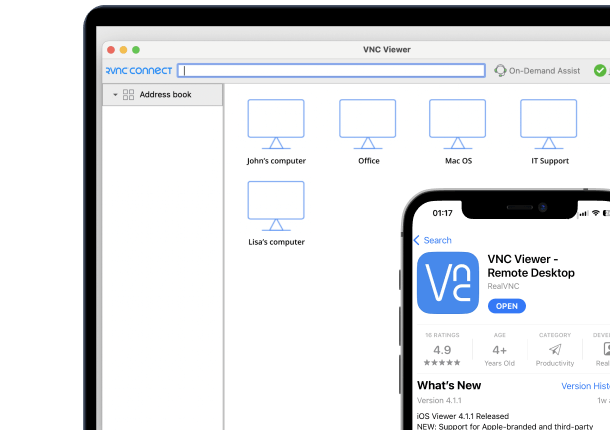
TightVNC and RealVNC were both born in the early 2000s. Since then, they’ve both gone down two very different roads. Both VNC solutions started out with the same goal: to make remote desktop access simple. They then took wildly different paths in terms of features, security, and user experience.
Fast forward to 2025, and a requirement for both fast and secure access to remote machines has redefined what remote access platforms look like. TightVNC has become one of the fastest and most widely used open-source VNC tools, while RealVNC prioritizes security and enterprise-grade remote access.
So, when it comes to RealVNC and TightVNC, which one should you choose? Both are solid options, but each shines in different areas. In this guide, we’re going to explore these two VNC options in depth. We’ll look at performance, security, and key features, so you can decide which VNC solution is the right fit for your team, setup, and business.
Understanding VNC and Its Role in Remote Desktop Control
Virtual Network Computing (VNC) is a technology that gives a user remote access to another computer’s desktop over a network. It works by transmitting the screen, keyboard, and mouse inputs from one device to another. This enables a user to remotely control a desktop as if they are sitting right in front of it.
For businesses, IT teams, and even individuals, VNC has become an essential tool for troubleshooting, accessing files, and providing support remotely. A VNC solution typically consists of a VNC client, or “viewer”, and a VNC server, which is installed on the machine requiring remote access.
Both developed at the same time from the original VNC and RFB protocol, TightVNC and RealVNC are two of the most popular and reliable solutions on the market today.
An Overview of RealVNC and TightVNC
The stories of RealVNC and TightVNC started at the same place: the lab at Cambridge in the UK. Here, the first version of VNC was created in the late 1990s. After AT&T closed down the lab in 2002, the original developers founded RealVNC. They took the original vision of remote access further with a strong emphasis on security, encryption standards, and commercial support.
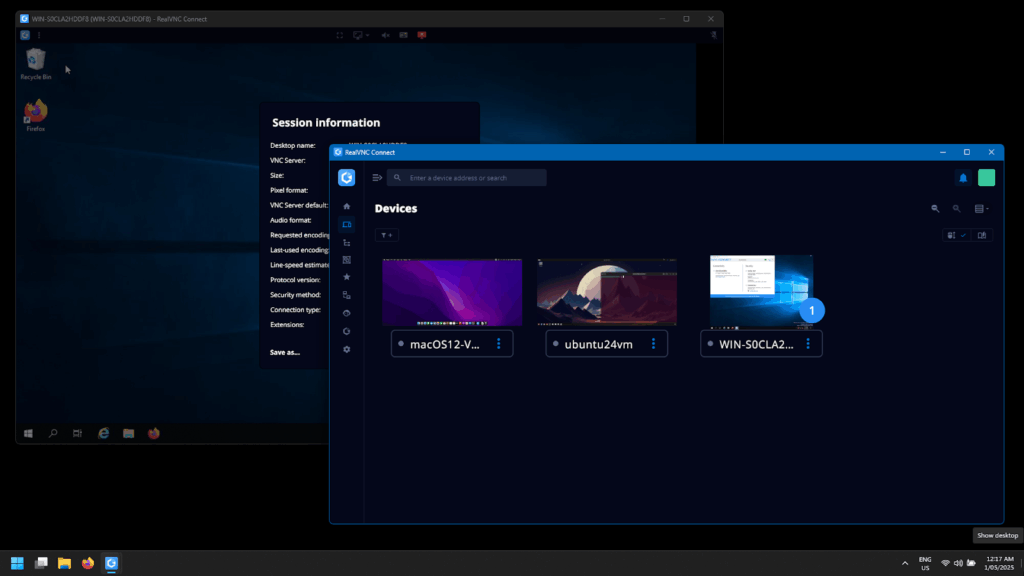
Meanwhile, TightVNC was developed as a community-driven fork of the original open-source code. It introduced tighter compression methods for better performance on slower connections. Over time, the TightVNC client and TightVNC server tools became known for simplicity, free availability, and backward compatibility, especially in educational environments.
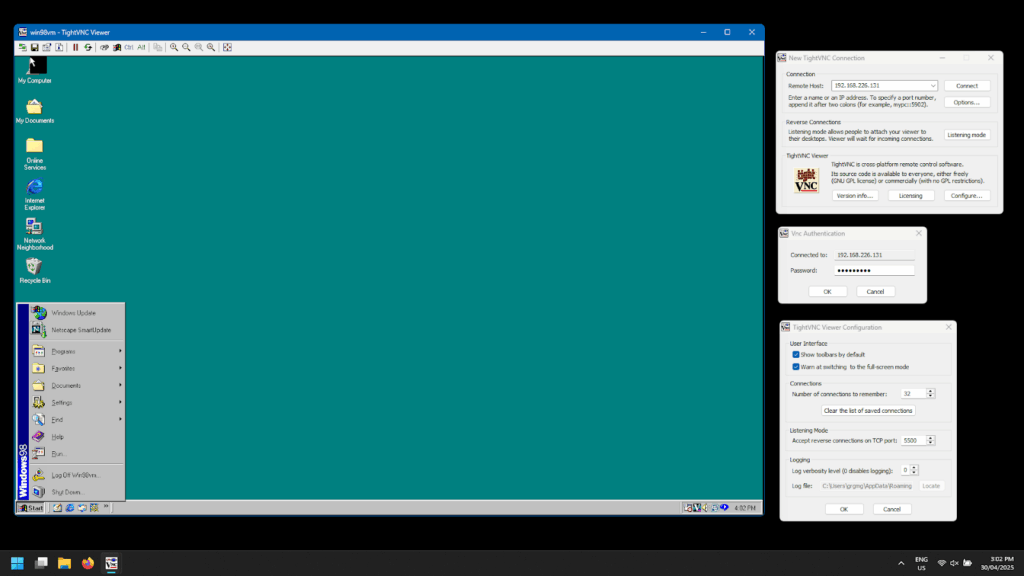
Both tools share common roots but their priorities have diverged significantly. In the next sections, we’ll break down how their features, performance, and security compare.
RealVNC and TightVNC Core Comparison Criteria
We will compare both RealVNC and TightVNC on five criteria that determine their real-world functionality in both enterprise and small-business environments:
- Features: This determines how much control, functionality, and flexibility you get from each tool.
- Performance: Whether or not the image quality of both tools is stable under various network connections.
- Security: How well each tool protects data in transit, password and authentication protection, and the amount of configuration required to adequately secure them.
- Ease of use: Evaluating how easy or difficult it is to install the remote control tools across different operating systems. Exploring which tool is compatible with which operating system.
- Use cases: Exploring which environments best suit the use of each tool, and which don’t.
Feature Comparison: What Can Each VNC Tool Offer You?
When taking a look at the features of RealVNC and TightVNC, it’s clear that both tools offer distinctly different experiences.
RealVNC Connect offers a full-featured platform that is purpose-built for enterprise environments. It supports cross-platform deployments across Windows Desktop and Server, macOS, Multiple Linux distros, Raspberry Pi, iOS, and Android. Users can directly connect to remote machines via LAN and VPN, or through RealVNC’s secure cloud platform, bypassing the need for port forwarding over NAT.
Key features include secure authentication, file transfers between different operating systems, session recording, real-time chat, and browser-based access. IT administrators benefit from centralized management tools, integration with Windows Domain environments, and simplified software updates.
In contrast, TightVNC is lightweight, free software with a bigger focus on simplicity. As an open-source tool, it supports the core VNC functions like file transfer, multi-monitor support, and desktop auto-scaling. One of the biggest features of TightVNC is the ability to place the viewer-side desktop into listening mode for reverse connections.
This feature makes it ideal for training or support scenarios where another user can connect and view the session. TightVNC also supports a Java viewer that enables cross-platform support on devices that support the Java framework.
Both tools support basic screen sharing and input control. However, RealVNC Connect’s added security and cloud-based VNC access set it apart for more demanding applications.
Performance Showdown: Which Tool Delivers Better Remote Access?
When it comes to performance, RealVNC Connect is designed with professional users in mind. Thanks to the standardized installer, it delivers a consistent remote control experience across Windows, macOS, Linux, iOS, and Android.
Under poor network conditions, the adaptive image quality technology adjusts on the fly, meaning that users are largely unaware of any changes in condition. For mobile applications and field work over cellular networks, support teams can troubleshoot with the confidence that a connection won’t drop out mid-way through an update or UAC prompt.
For work environments where accuracy and low lag are crucial, such as CAD and design applications, RealVNC also excels. It maintains responsiveness during sessions and is suitable for demanding tasks like high-speed streaming and real-time collaboration.
TightVNC helps improve performance on slower connections via its “tight” encoding. This is a combination of JPEG and zlib compression that is optimized for lower bandwidth environments. While it is technically possible to stream video or even stream DirectX games, it’s still limited to low frame rates. Still, for simple desktop access or light troubleshooting tasks over local networks, it remains a capable tool.
For enterprise environments, RealVNC Connect’s cross-platform performance gives it a clear edge. For smaller tasks, TightVNC still gets the job done, especially when bandwidth is a concern.
Security Features: Keeping Your Connections Safe with VNC
Security is a core differentiator between RealVNC Connect and TightVNC. The gap is quite significant.
RealVNC Connect prioritizes enterprise-grade protection by default. All connections are encrypted end-to-end using 256-bit AES encryption. Session content is never visible to third parties, not even to RealVNC itself.
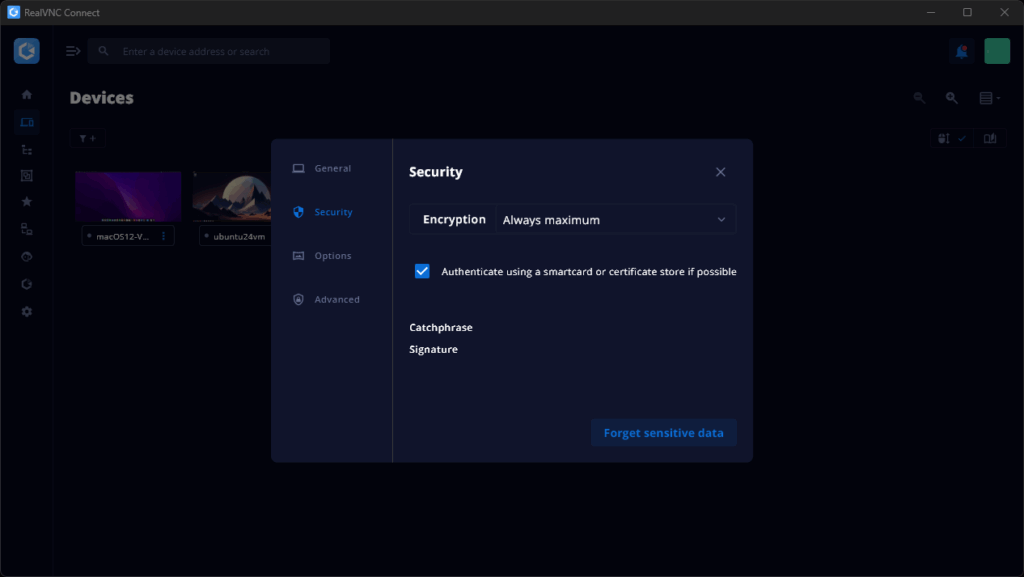
Additional controls include strong password protection, multi-factor authentication, single-sign-on (SSO), and support for VPN use. Administrators can configure granular access control policies, which makes it an ideal choice for MSP support teams and businesses that handle sensitive data.
When it comes to TightVNC, there’s not a lot to talk about. The VNC password itself is encrypted using a DES-based scheme but the rest of the session is completely unprotected. Official recommendations for security hardening for TightVNC sessions over public-facing internet are to tunnel through SSH or only use it on internal networks. TightVNC does, however, provide basic access control via IP allow and block listings on the server side itself.
How Easy Are They to Use? VNC Software Designed for the End User
In terms of how easy each remote access solution is to install and use, RealVNC Connect delivers a polished and intuitive experience right out of the box. Installation and setup of both server and viewer is quick as both Windows and Mac have combined installers.
Even on Linux, where remote access setups are notoriously difficult, RealVNC Connect installs easily without the usual digging into config files.

The interface is sleek and features dark mode and user-friendly controls that make using RealVNC Connect feel more like a modern application.
On the other hand, TightVNC has a more straightforward, no-frills user interface. It’s remarkably easy to install on both Windows and macOS, but the experience does become significantly more complicated on Linux.
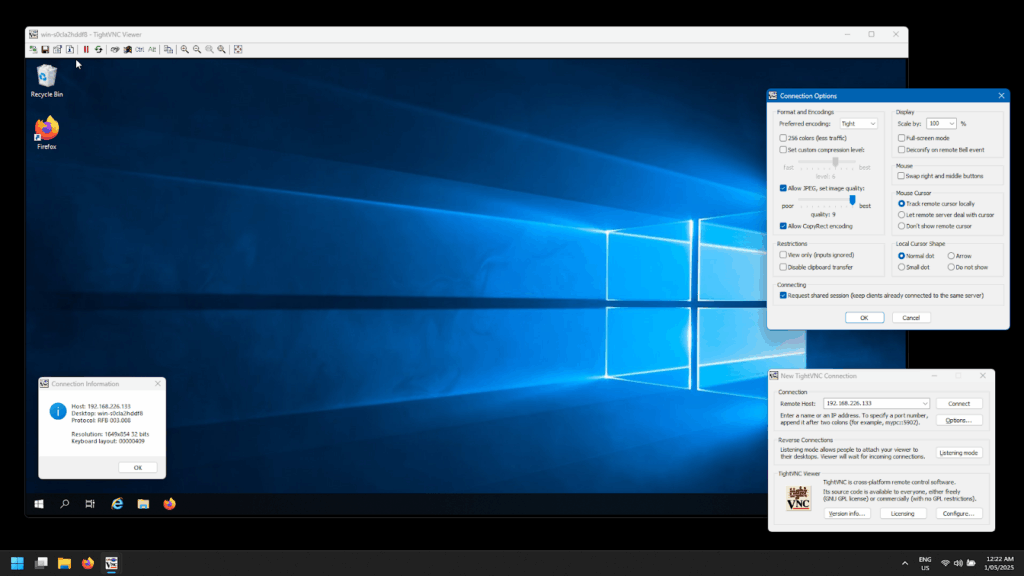
Setting up the TightVNC server requires a lot of additional configuration, particularly with systemd settings. This makes it a bit less beginner-friendly for users unfamiliar with Linux.
Best Use Cases: When to Choose RealVNC or TightVNC
The choice between RealVNC Connect and TightVNC really comes down to your priorities. Larger businesses are likely to require a more security-focused approach to remote access, whereas individuals and smaller businesses might just want basic remote control functionality.
RealVNC Connect is well-suited for:
- Businesses that demand secure, cross-platform access across multiple operating systems, including iOS and Android.
- IT teams that manage remote devices at scale need centralized control with auditing for remote employees and workstations.
- Organizations with strict compliance standards that require end-to-end encryption as standard.
- Support environments involving mobile platforms like iOS and Android, or hardware such as Raspberry Pi.
TightVNC is ideal for:
- Home users or small teams looking for something free and flexible that requires minimal setup.
- Developers or hobbyists running projects on Lightweight Linux distros or legacy operating systems.
- Users who are comfortable with SSH tunneling and manual configuration to secure VNC sessions.
While each tool has its strengths, the right choice depends on the use cases that matter most to your business environment.
Pros and Cons: RealVNC and TightVNC at a Glance
Both RealVNC and TightVNC deliver effective remote access solutions, but their value depends heavily on your priorities. Whether you need enterprise-level control or a simple VNC setup for home use, understanding the trade-offs is key.
Below, we’ve created a table to summarize the pros and cons of each platform:
| RealVNC Connect | TightVNC | |
| Pros | Strong security: 256-bit encryption, MFA, SSO | Completely free and open source |
| Seamless deployment on Windows, Mac, Linux, iOS, Android, Raspberry Pi | Lightweight performance on low-spec machines and local network setups | |
| Enterprise features: file transfer, session recording, chat | Reverse connections and Java viewer for flexible remote control | |
| Centralized admin tools for managing many clients | Supports multi-monitor setups | |
| Active development and professional support | Ideal for Linux users and technical setups |
| RealVNC Connect | TightVNC | |
| Cons | Full feature set requires a paid license | Limited security unless paired with SSH or VPN |
| Can be overpowered for basic remote access needs | No official support for macOS and Windows servers | |
| Some advanced settings may require admin experience | Lacks enterprise-level features and centralized management | |
| Cloud-based access may raise concerns for privacy-conscious users | Setup complexity increases with secure connections |
How to Choose the Right VNC Tool for Your Needs
When weighing the various VNC solutions available, be that RealVNC, TightVNC, or any other solution for that matter, start with your priorities.
If security is absolutely required and you need advanced management features like centralized management and mobile access, RealVNC is the clear fit. This is especially true for businesses and IT teams. It’s built for professional environments where compliance, scale, and support really matter.
TightVNC is a strong option for those who value simplicity, open-source software, and, of course, zero cost. It works well for personal use, lightweight projects, or for tech-savvy admins who are comfortable with SSH tunneling and manual setups.
RealVNC Connect or TightVNC? Which Is Right for You?
The right between the two really comes down to how you and your business plan on using remote access. RealVNC Connect stands out with its advanced security, full feature set, and standardized experience across all platforms. It’s the ideal solution for businesses, IT teams, and professionals for whom reliable and scalable remote desktop control is a priority.
TightVNC has its place amongst users who want a free and lightweight solution without the bloat of enterprise-grade features. In the end, both are capable tools that have withstood the test of time. Take the time to test each and see which ones will ultimately suit your needs best.
You can start testing RealVNC Connect right away by downloading and installing the server and client for Windows, macOS, and Linux.
Frequently Asked Questions about RealVNC Connect and TightVNC
What is the main difference between RealVNC and TightVNC?
The main difference between TightVNC and RealVNC is the feature set. RealVNC Connect offers advanced features and strong security by default, making it more suited to business and corporate environments. TightVNC is free and open-source but lacks advanced features. It is best suited for personal and small-scale use.
Is TightVNC secure enough for business use?
TightVNC lacks any kind of built-in encryption or the ability to configure it. To secure TightVNC sessions, the VNC stream must be tunneled through SSH or a private VPN. By default, this makes TightVNC not secure enough for business use.
Does RealVNC support mobile devices?
Yes! RealVNC Connect supports mobile access on both Android and iOS. This allows remote control of devices from tablets and smartphones.
Which tool is better for beginners?
Despite the extensive feature set, RealVNC Connect is easier for beginners due to its streamlined installation and intuitive interface. TightVNC may require some more technical setup.
Can both tools be used for cross-platform remote access?
Yes, both RealVNC Connect and TightVNC support multiple operating systems, including Windows, macOS, and Linux. RealVNC Connect does offer a smoother experience across multiple devices, with installation and user interface being standardized across multiple devices.