Maybe you’ve taken another look at VNC after one too many frustrating RDP sessions. Or maybe you just want a remote desktop solution that supports more than just one OS at a time. Either way, the search for the best VNC server tends to always start the same way—with a long list of solutions that all promise easy remote control but vary wildly in reliability and security.
This guide takes a look at what to look for in a VNC server and compares the leading options. We’ll also highlight why RealVNC Connect is the only real enterprise-ready remote access solution when it comes to security and cross-platform support.
Key Features to Look for in a VNC Server
Not every VNC server is built with the same priorities in mind. What works great for controlling a computer across the room might not meet the requirements of a team managing hundreds of devices across the country.
When considering various VNC options, these are the core features that define an ideal VNC server for business use:
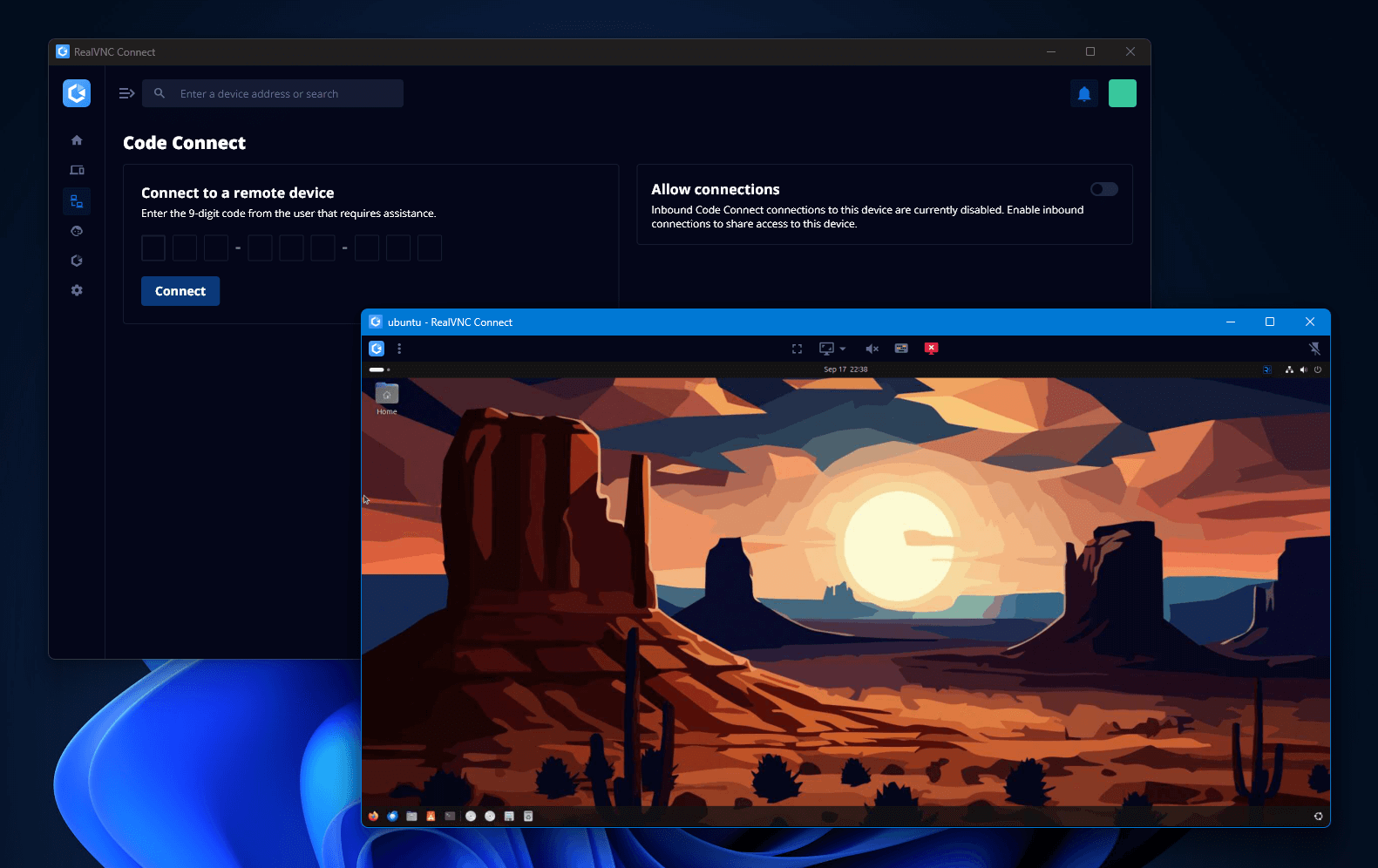
- Security and Access Control: Take a close look at encryption. Look for TLS encryption as a minimum, multi-factor authentication, and granular control over user permissions. Modern VNC solutions like RealVNC Connect have these security features built in. Additionally, it offers the ability to create ad-hoc connections with a token rather than exposing IP addresses via the Code Connect feature.
- Multi-Platform Support: A modern solution needs to consider the needs of all operating systems. A VNC server on a Mac should be accessible by a Windows machine. A Linux Ubuntu desktop should be able to seamlessly interact with a VNC server on a Windows server or even iOS and Android.
- Unified Application Experience: The best VNC solutions should combine the viewer and the server into one application. Doing so reduces complexity for IT professionals who need to deploy and manage the software and standardizes encoding and performance.
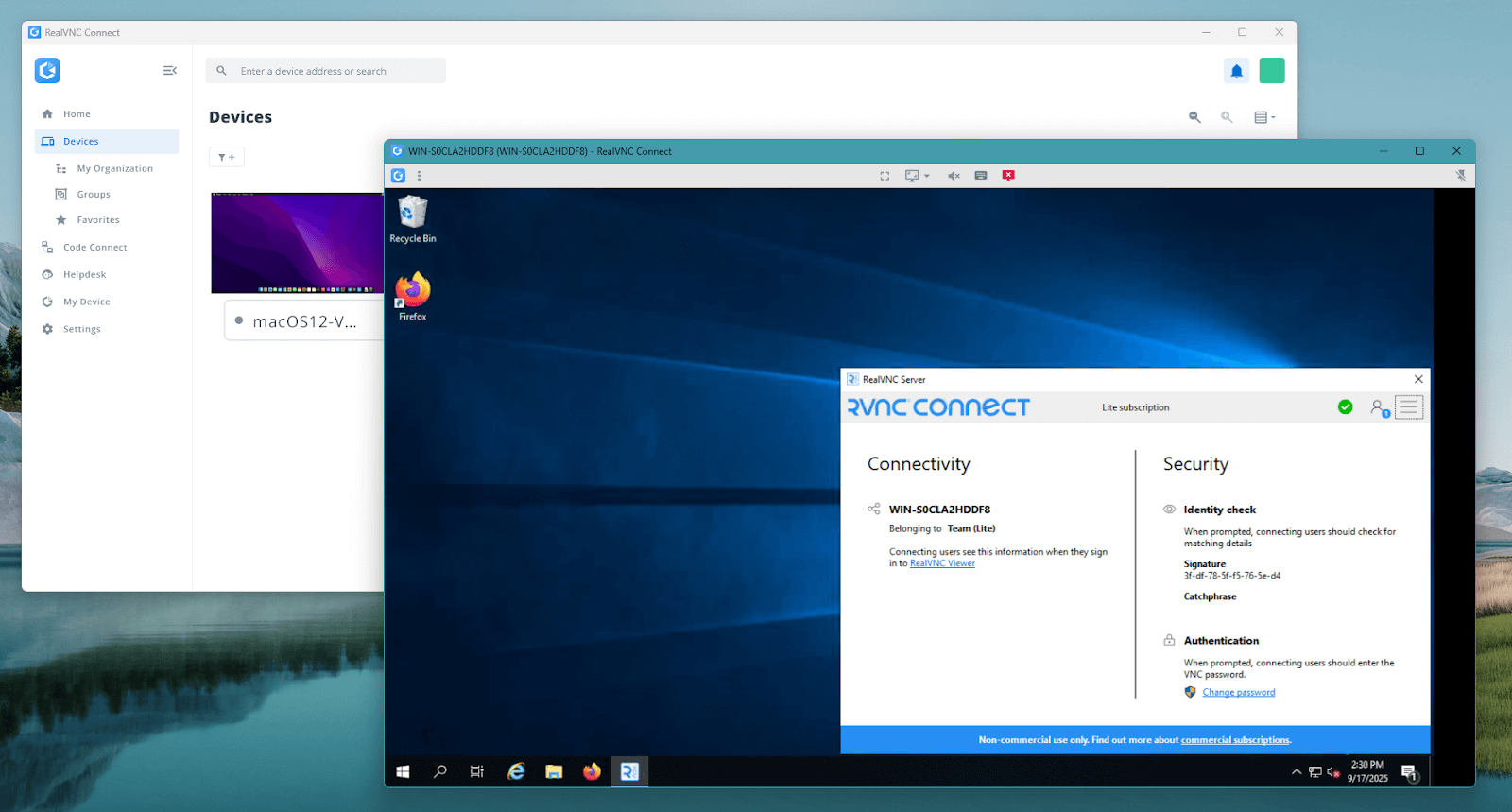
- Enterprise Scalability: IT teams need to be able to deploy the VNC platform from application packagers like SCCM and InTune. Installation should also be free of complicated custom scripting or configuring machines one by one after imaging. RealVNC Connect’s Management Console allows for centralized management of all endpoints as well as policy enforcement and audit logging.
Keep these criteria in mind, and it will become easier to separate the basic tools from platforms built for enterprise.
Top 5 VNC Server Solutions in 2025
Since the advent of the VNC protocol in the 1990s, VNC solutions have adapted and grown into fully-fledged remote desktop solutions. Some tools remain lightweight and free and are built more for hobbyists or legacy computers. Others have a strong focus on supporting specific operating systems and more modern functionality.
In this section, we’re looking at the best VNC options for a wide variety of real-world applications. Each has its strengths and limitations, from basic remote support for home users to advanced features like cloud brokering and audit logging.
1. RealVNC Connect – Best for Enterprise Security and Mobile Devices
RealVNC knows VNC. As the original developers of the VNC protocol back in the 1990s and 2000s, the RealVNC Connect remote access solution is the best adaptation of the original platform.
RealVNC Connect combines server, viewer, and management console functionality into one intuitive application and extends support across both desktop and mobile devices. Its enterprise-ready design includes TLS 1.2+ encryption out of the box, support for SSO, and multi-factor authentication.
Its centralized console onboards and configures endpoints effortlessly, tracks assets, and enforces your security and data protection policies. Features such as file transfer, remote printing, and Code Connect guest access make it the most practical option for both IT professionals and end users.
What sets RealVNC Connect apart from other VNC tools is the VNC Cloud feature. This cloud connection broker means that machines connected to the management console don’t need direct IP access to establish connections. With VNC Cloud, remote sessions can be established behind firewalls, proxies, and NAT without the need for port forwarding, risky firewall rules, and a DMZ.
- Supported OS: Windows, macOS, Linux, Raspberry Pi, iOS, Android
- Limitations: Advanced enterprise functions require initial integration with existing infrastructure.
2. TightVNC – Best for Legacy Systems Remote Support
TightVNC is a lightweight option that is widely used to maintain older computers and systems. It runs on both Windows and Linux, making it appealing to hobbyists, labs, and smaller teams that need simple remote desktop access.
Its community-driven nature keeps it relevant for basic tasks, but its complete lack of built-in transport encryption makes it not ideal for enterprise use.
- Supported OS: Windows, Linux
- Limitations: DES-based password protection, unencrypted session traffic without SSH tunneling, poor multi-monitor support, community-only updates, and no advanced features or access control beyond password protection.
3. UltraVNC – Best for Windows Environments
UltraVNC server is a long-standing VNC server built primarily for Windows environments. Unlike other open-source VNC solutions, it can support encryption and authentication over Windows Domain networks via MS Logon I and II.
It also supports more modern features like chat, file transfer, and multi-monitor support. It’s a flexible and high-performance VNC server that’s suited for smaller organizations that still want a free and open-source option.
- Supported OS: Windows (but the client is compatible with other VNC servers on Linux)
- Limitations: The server can only be installed on Windows machines, and the official website doesn’t have extensive documentation.
4. TigerVNC – Best for Linux Desktops
TigerVNC is a well-maintained fork of TightVNC that’s designed for both modern and legacy desktop environments, particularly Linux. It delivers much better performance than its predecessors and supports relatively good encryption via a plugin.
The X11 version of X0vncserver supports extremely old Linux window managers without replacing their existing sessions. Its flexibility is appealing to teams that need a free solution to switch between window managers on Linux while handling newer graphics stacks.
- Supported OS: Linux with limited support for Windows via community builds.
- Limitations: Weak security defaults that need extensive hardening before use in a corporate environment. No real server support for Windows or macOS.
5. Vino – Best Native VNC for GNOME Desktop
Vino is the default VNC server that comes with Linux distributions using the GNOME desktop environment. As it’s pre-installed, users only need to enable it via the settings menu and supply an IP address for any VNC client to connect to.
For enthusiasts or smaller businesses with a Linux desktop fleet, Vino offers a simple way to facilitate remote access. At its default settings, it requires encryption to establish a connection, which gives it slightly better turnkey potential than TightVNC and UltraVNC.
- Supported OS: Linux with the GNOME desktop environment
- Limitations: The product has extremely limited features and requires manual enabling to function properly. Development has slowed in favor of RDP in the Mutter window manager shipped with the latest Ubuntu LTS.
Best VNC Server Selection Guide: Evaluation Framework
A quick checklist beats guesswork. Use this framework to compare VNC servers with the same criteria your team will rely on in production:
- Security First: Look for strong TLS, MFA, and audit-ready logging.
- Supports Multiple OSs: Verify the VNC server supports all platforms your business maintains.
- Performance: Stable over any network and can handle latency and bandwidth limits.
- Usability: A clear and modern UI, fast setup, and a reliable solution for admins and users alike.
- Integration: Works with your identity provider and ticketing stack.
- Trial it first: Run a demo in real workflows. Measure reconnects, file moves, and browser logs for sufficient detail.
- Benchmark: Use RealVNC Connect as the reference for enterprise-grade security, control, and scalability.
Conclusion
The best VNC server balances strong security, advanced features, and the ability to scale up and down with demand. Encryption, centralized management, and integration with current workflows are all must-haves in modern business environments.
If frustrations with RDP and other tools have led you to consider VNC for remote desktop access, download and start your free trial of RealVNC Connect. You’ll see what a truly secure and enterprise-ready VNC platform looks like before investing time in less capable tools.
FAQ
What makes a VNC server secure for enterprise remote desktop use?
A VNC server must have encryption enabled, authentication, and full audit access logs to be considered secure for enterprise use. Currently, the only VNC server that provides this security by default is RealVNC Connect.
How does RealVNC Connect simplify remote access management?
RealVNC Connect centralizes policy control, user permissions, and reporting within its management console. Admins can manage large fleets of remote machines without scripting or manual setup.
Can VNC solutions support both legacy and modern operating systems?
Yes, open-source tools like TightVNC can run on legacy systems as old as Windows NT and low-resource Linux distributions with backwards-compatible server and clients.
What are the key differences between open-source and commercial VNC servers?
Open-source tools don’t require licensing and payment, whereas a commercial VNC server like RealVNC Connect requires a subscription. Licensing isn’t the only difference, however. Open-source tools like TightVNC require more maintenance and configuration to be considered enterprise-ready. Commercial VNC servers, on the other hand, offer compliance-ready features, guaranteed updates, and extensive customer support.