Remote desktop technologies are essential tools for modern businesses, enabling seamless remote work, efficient support, and effective collaboration.
Two common terms you may hear in this space are Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) and Remote Desktop Connection (RDC). While these acronyms are sometimes used interchangeably, they refer to distinct components within remote access.
Understanding the nuances between these technologies can help you choose the right solution to meet your specific needs.

What is remote desktop protocol (RDP)?
Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) is a proprietary protocol developed by Microsoft to provide remote access to computers and servers. You can control a remote machine as if you were sitting in front of it.
Here are the key features of RDP:
Secure: RDP uses strong encryption and multi-factor authentication. It also supports Network Level Authentication (NLA), which adds an extra layer of security by requiring the user to authenticate before a remote session is established.
Flexible: RDP works with various Windows operating systems and can also work with other operating systems using third-party software.
Fast: Optimized for high performance with low latency, RDP can handle tasks over remote connections even in low bandwidth situations.
RDP is used for remote administration, virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI), and remote support. It’s particularly useful in environments where secure and fast remote access to a network or system is critical.
What is remote desktop connection (RDC)?
Remote Desktop Connection (RDC) is a feature built into the Windows operating system that uses RDP to connect to remote computers. It provides a graphical interface for users to access and control remote machines.
Here are the key features of RDC:
Simple: RDC has a user-friendly interface built into Windows so users can set up and use it without extensive technical knowledge.
Accessible: You can access from any Windows device, so users can connect to their work computers from home or other remote locations.
Integrated: Seamlessly integrates with other Microsoft services, so if you are already in the Microsoft ecosystem, it’s a cohesive experience.
RDC is perfect for individual users who want to connect to their work computers from home or IT professionals managing multiple devices in a network. Its simplicity and integration with Windows make it a great choice for many users.
Key differences between RDP and RDC
While RDP and RDC are related, they are not the same. Here are the differences:
Technology and architecture: RDP is the protocol under the remote connection, and RDC is the client application that uses RDP. RDP can be used by other client applications, not just RDC.
User experience: RDC has a simplified interface, so it’s user-friendly and accessible for nontechnical users. RDP has more control and customization options, which is good for advanced users and administrators.
Performance: Both RDP and RDC are high performance but RDP’s advanced features can be more optimized in complex environments. RDP’s performance is enhanced by RemoteFX which improves the graphical experience over remote connections.
Security: Both have robust security features, including encryption and multi-factor authentication. But RDP has NLA (Network Level Authentication) which adds an extra layer of security. Best practices for secure usage are necessary to mitigate vulnerabilities.
Compatibility: RDP supports many devices and operating systems, including Windows, macOS, Linux, and mobile platforms through third-party clients. RDC is designed for Windows environments but can also be used with the Microsoft Remote Desktop app on macOS.
Benefits of remote connection tools

Remote connection tools like RDP and RDC have many benefits:
Cost reduction: Remote connection tools can reduce the need for physical office space and travel expenses. Employees can work from anywhere, with no need for permanent desks and large office spaces.
Increased security: While remote work brings new security challenges, remote connection tools with advanced security features can protect sensitive data. Encryption, multi-factor authentication, and secure access protocols are necessary to maintain security.
Flexible working: These tools allow employees to work from anywhere, increasing productivity and job satisfaction. Flexible working can also make a business more resilient to disruptions such as natural disasters or pandemics.
Better collaboration: Facilitate remote team collaboration. Features like real-time screen sharing, file transfer, and integrated chat can improve communication and teamwork.
Remote access methods

Knowing the different remote access methods can help you choose the right one for you:
Direct access: Connects directly to a remote device. Users can control the device as if they are physically present. This method is simple and good for simple remote control scenarios.
Indirect access: Uses an intermediary server to relay data between devices. This method is good for complex environments where direct connection is not possible.
VPN (Virtual Private Network): A virtual private network (VPN) enables secure data exchange by creating a secure private connection between two devices. In simple terms, it builds a private tunnel between the two devices whereby all exchanged data is protected by a layer of encryption.
Types of remote access technology
RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol): Optimized for Windows environment, RDP provides robust remote control and supports multiple devices and operating systems.
VPN (Virtual Private Network): As we mentioned earlier, a VPN connection is sometimes understood as providing the remote user with a tunnel into the internal IT ecosystem of an organization. Users can then access tools and resources as they would in-house.
VPNs have been around for a while now and are understandably very popular. They offer security via encryption balance with flexibility. The result is that it’s easier to shift files between local and remote networks.
However, VPNs can be difficult to set up, sometimes requiring significant technical expertise.
Furthermore, a VPN doesn’t give remote users access to the remote desktop of a specific device. Instead, users can access the tools and resources on a remote network more generally.
Secure remote access: Secure remote access provides users with direct control of a device that’s elsewhere, allowing them to interact with that device as if they’re sitting in front of it. At the same time, someone else literally sitting in front of that device would be able to watch the remote user’s actions.
With a VPN connection, a remote user connects to a network rather than a specific device. But with secure remote access (and RDP, as well), you can view and control a specific device.
This makes secure remote access a powerful business tool. For instance, remote workers can access their office computers even when they’re working from home, and IT support staff can troubleshoot an employee’s computer (or mobile, tablet, or other device) no matter where either individual is based. This supports flexibility and keeps employees productive.
Secure remote access connections are generally facilitated by specialist software. Remote access software takes care of the technical steps involved in remote connection, making it a convenient option for a wide range of users.
Of course, for security reasons, keeping any remote access software up to date is essential and ensuring all the latest patches are installed.
What are remote desktop services (RDS)?
Remote Desktop Services (RDS) are a set of components in the Microsoft Windows operating system. It’s underpinned by Microsoft’s Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP), mentioned above.
A core benefit of these components is that they allow users to connect with a desktop remotely from whatever physical device they’re using. Once connected, users can interact (remotely) with that desktop.
RDS system permissions dictate the experience, however, in theory, individuals can use the remote desktop (including access to all its software, files, and tools) as if it’s installed on the machine they’re sitting at.
However, RDS does have limitations. One is that it doesn’t support effective screen-sharing, which can reduce its business applications. Screen-sharing technology benefits collaboration and tech support, for example.
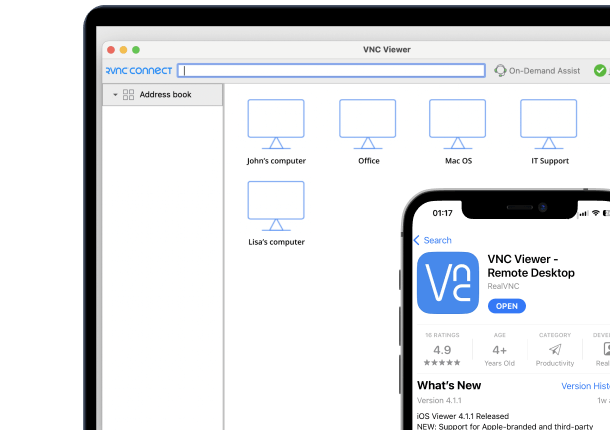
Remote access software from RealVNC
RealVNC offers powerful remote access software, enabling users to remotely control computers. It’s a convincing alternative to both RDS and VPN.
RealVNC’s flagship product, RealVNC Connect, makes it easy for businesses to provide secure remote access and support from anywhere. The highly flexible and customizable system works across a wide range of platforms and operating systems, making it a convenient choice for any business. It also offers multiple security options, which is crucial in today’s digital-first world.
RealVNC Connect delivers high-quality, smooth, and responsive remote connections. You’ll feel like you’re right in front of the host device, especially with its remote desktop capabilities.
Additionally, RealVNC’s software makes screen-sharing collaboration across your teams easy. For instance, IT support staff can access an employee’s device and fix an issue while the employee watches. Want to explore RealVNC’s capabilities for yourself? Get started with a free trial!