What happens when a hospital bed becomes smarter than your average laptop? Welcome to the era of IoT in healthcare, where sensors, wearables, and smart machines connect entire clinical ecosystems.
Where ICU telemetry, remote diagnostics, and connected devices are generating vast volumes of health data and helping physicians intervene earlier, hospitals operate more efficiently, and patients receive personalised care outside traditional clinical settings. That’s IoT.
The numbers speak for themselves: the global healthcare IoT market is poised to grow from $127.7 billion in 2023 to $289.2 billion by 2028, at a CAGR of 17.8%. But behind the growth, integration is difficult, security is non-negotiable, and legacy systems are still everywhere.
So, if you’re evaluating platforms or planning your digital health infrastructure, this guide is built to support informed, high-stakes decisions about IoT in healthcare.
How does IoT in healthcare work? (and why it’s difficult to implement it)
The Internet of Things (IoT) in healthcare is a system of interconnected devices (like wearable heart monitors, infusion pumps, smart imaging systems, etc.) all communicating in real time across local networks or the cloud. These devices collect healthcare data like patient vitals, machine telemetry, or room occupancy data and transmit it for analysis, display, or storage.
But while the vision of connected care is compelling with IoT devices, the implementation is anything but straightforward.
What IoT in healthcare really means
IoT in healthcare allows medical devices and systems to collect, transmit, and sometimes analyze health-related data without direct human input. Think of a smart bed that adjusts pressure to prevent bedsores and logs those micro-adjustments automatically into a patient’s digital chart. Or a remote monitoring glucose device that alerts both patient and clinician if levels deviate from a healthy range.
These devices fall into certain categories:
- Wearables like fitness trackers and ECG patches
- In-room systems like connected beds and infusion pumps
- Backend infrastructure like environmental sensors or telemetry dashboards
- Remote diagnostics tools supported by secure remote access software like RealVNC Connect
Together, these tools aim to improve care, reduce human error, and help improve patient outcomes with better decision making and lower healthcare costs.
Why is implementation so complex?
The promise of IoT is clear, but turning that promise into practice often collides with an imperfect reality:
- Firstly, legacy systems: Many hospitals still run critical systems on outdated software or bespoke devices with proprietary interfaces. Integrating these with modern IoT ecosystems is a constant headache.
- Secondly, inconsistent protocols: There’s no single “IoT language.” Devices from different vendors may not speak to each other without custom middleware tech or a core medical system.
- Lastly, security gaps: Every new connected device introduces another attack surface and can potentially endanger data collected from patients. Without proper segmentation and access control, a single unpatched device can compromise data security.
Core benefits of IoT in the healthcare industry
The promise of IoT in healthcare is bold. Still, in our experience, IoT truly allows hospitals to move from reactive to proactive care and more informed decisions when implemented correctly. Here are the top benefits:
1. Continuous patient monitoring
Wearable devices and remote sensors help monitor patient health 24/7, from heart rate and blood oxygen levels to sleep patterns and respiratory activity. This uninterrupted stream of data helps:
- Detect early warning signs before a condition escalates
- Prepare for timely interventions (especially for chronic disease patients)
- Support post-discharge recovery with remote oversight
2. Operational efficiency and cost reduction for both healthcare providers and patients alike
Hospitals are super complex operational ecosystems. IoT helps them run smarter.
Smart asset tracking, automated temperature monitoring for vaccines, and predictive maintenance for medical equipment cut down on wasted time, human error, and resource drain. And by digitising routine tasks, care teams can focus more on patients and less on paperwork or manual device checks.
McKinsey estimates that IoT could generate up to $12.6 trillion in global value by 2030, with healthcare accounting for 10–14% of that total.
3. Data-driven decision making for healthcare professionals
More data isn’t always better. But better data, delivered in real-time, is a no-brainer. When integrating internet of things feeds with analytics platforms, hospitals can gain tangible outcomes like:
- Real-time dashboards for ICU management
- Predictive insights for triage or patient flow
- Historical data trends to refine treatment protocols
For example, when glucose monitors sync with EHR systems, endocrinologists can see how diet, sleep, and medication interact. For a diabetic, such insights make their medicine more personal and precise, and that translates to better quality of life and even longevity.
4. Better connectivity and clinical collaboration
When clinicians, nurses, and support staff can access the same patient data from different floors, wings, or even facilities, collaboration becomes so much better. And when secure remote access tools like RealVNC Connect are in place, that coordination extends way past the hospital walls, all the way to healthcare provider chains and customers’ mobiles.
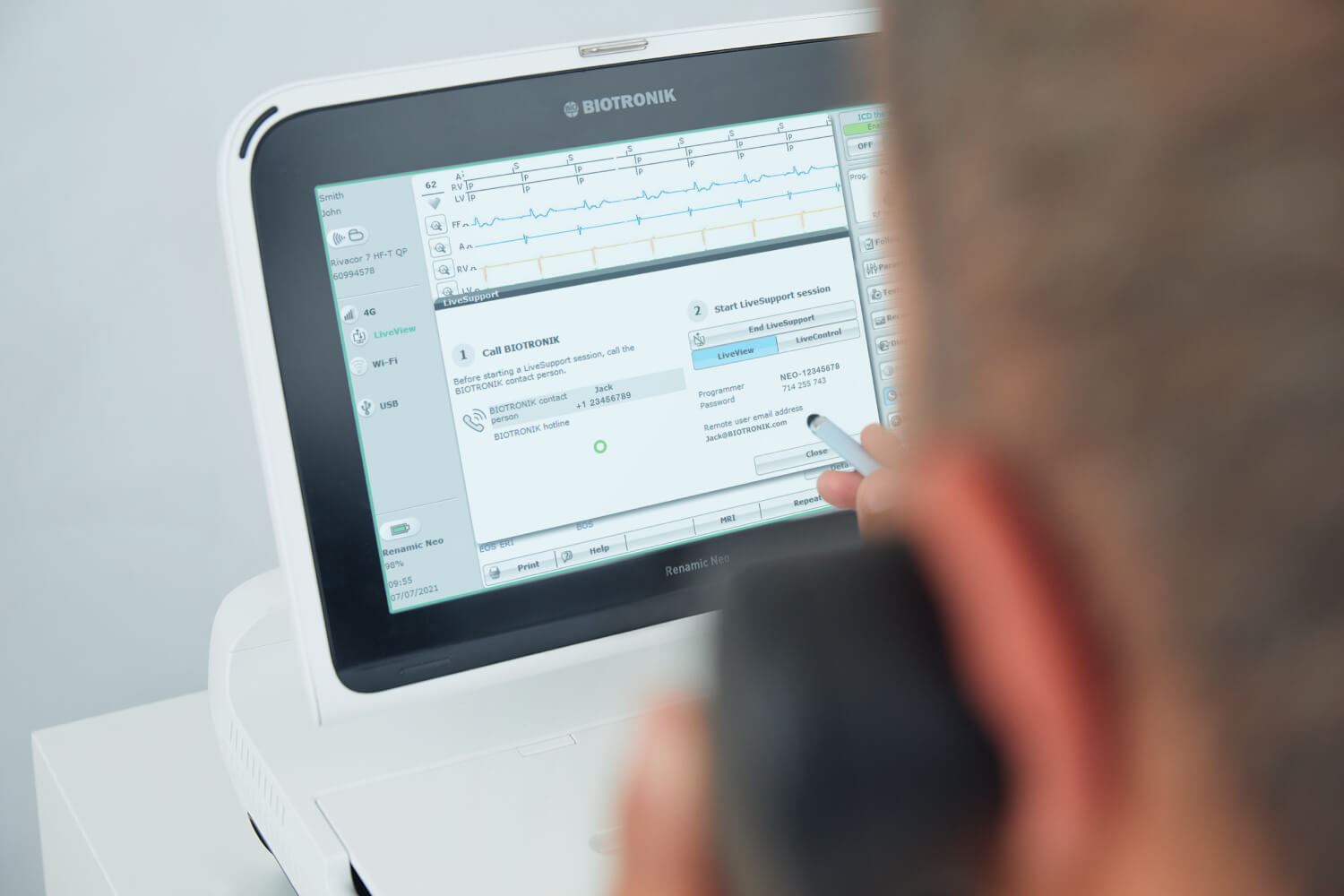
Take BIOTRONIK, for example. Their cardiac device support team once relied heavily on phone consultations, often requiring unnecessary travel and coordination with both clinicians and patients. Now, using their LiveSupport product, based on RealVNC Connect, they can securely access programming devices like the Renamic Neo in real time, directly from Berlin or anywhere else.

Similarly, at Southern Ohio Medical Center, the IT team supports over 2,000 medical systems across departments without having to be physically present. With RealVNC, a technician can instantly access a physician’s workstation to resolve issues or assist with training.
Applications and use cases in healthcare with IoT
The Internet of Things in healthcare is an ecosystem of technologies that make the healthcare industry more patient-oriented. Here are some of the most common tech and devices that make it happen.
1. Remote patient monitoring
Remote patient monitoring is one of the most widespread applications of IoT in healthcare. Devices like smart heart rate monitors, blood pressure cuffs, or continuous glucose monitors collect vital signs in real time and transmit them securely to care teams.
These devices continuously collect vital metrics like heart rate, oxygen saturation, glucose levels, and transmit them to care teams in real time.
The clinical potential is real. In a large-scale study using wearable tech, 34% were confirmed to have atrial fibrillation after ECG monitoring. The alerts had an 84% positive predictive value.
In a hospital setting, this data-driven approach means fewer unnecessary visits, faster interventions, and safer, more personalized care.
2. Telemedicine & virtual consultations
IoT devices have the power to create a clinically viable remote experience. Smart spirometers or Bluetooth-enabled otoscopes feed patient data live to physicians during teleconsults. For rural or mobility-challenged patients, this is no less than a lifeline.
For example, at Southern Ohio Medical Center, the IT team supports over 2,000 medical systems across departments without having to be physically present. With RealVNC, a technician can instantly access a physician’s workstation to resolve issues or assist with training.
Such medical IoT devices also have the potential to improve efficiency for customers, as they reduce healthcare costs associated with transportation, accommodation, and in-person appointments.
3. Smart medical devices & wearables
Think of smart inhalers that track medication or implantables that send real-time alerts to cardiologists. Such IoT medical devices are truly changing what continuous health monitoring and medical data collection mean. Plus, IoT-powered devices personalize care.
4. Predictive maintenance of medical equipment
Medical IoT keeps machines healthy too.. Connected sensors embedded in imaging systems, dialysis machines, or ventilators can detect performance anomalies before they escalate into failures.
For hospitals, this helps minimize downtime, extend the life of expensive equipment, and prevent care disruptions in critical units like radiology or the ICU.
5. Data integration for clinical decision-making
IoT generates mountains of data. But the magic happens when the integration of data generated from patient monitoring, electronic health records, wearable devices, and medical equipment is seamless.
That’s when IoT platforms help clinicians see the full picture. For example, trends from glucose monitoring devices, cross-referenced with medication data from an EMR, can trigger smarter insulin adjustments.
For healthcare professionals, being able to access real-time dashboards remotely becomes synonymous with patient safety, better treatment outcomes, and efficiency.
Challenges and limitations of IoT in healthcare
IoT in healthcare comes with a list of important challenges.
1. Interoperability and standardisation
One of the biggest hurdles for healthcare professionals and IT leaders is the lack of common standards across IoT devices. A hospital may deploy blood pressure monitors from one vendor, glucose monitoring devices from another, and smart beds from a third party producing data in incompatible formats.
This fragmentation slows down real-time monitoring, complicates integration with electronic health records, and makes patient data mining harder. Without standardised APIs or communication protocols, health systems risk ending up with siloed data lakes that nobody can truly use.
2. Data overload and analysis fatigue
Remote patient monitoring generates enormous volumes of health data. Think heart rate, oxygen levels, body temperature, blood sugar levels, and more…they’re generated on a continuous basis. But data collected ≠ insight.
Without strong infrastructure for data processing, secure storage, and advanced analytics, healthcare providers face raw biometric data with no way to act on it. False positives, alert fatigue, and misinterpreted signals can reduce treatment outcomes and strain clinical teams, as well as interfere with medical history inaccurately.
As McKinsey says, the real value of IoT lies in how well that data is turned into actionable insight, rather not just how much is collected.
3. Infrastructure and cost barriers
Deploying IoT in healthcare involves investment in secure networks, cloud computing platforms, real-time monitoring systems, and training across the care continuum. Many hospitals, especially in rural or public settings, still rely on legacy IT and paper-based medical records.
High upfront costs, slow procurement cycles, and regulatory complexity also slow down adoption. The solution is to start small and scale strategically and prioritize systems that offer immediate ROI, minimal disruption, and strong security out of the box.
For example, RealVNC Connect V8 is lightweight enough to run on existing infrastructure, including ARM-based devices or headless Linux systems often found in labs and diagnostics. It allows IT teams to remotely configure and troubleshoot devices without needing to travel onsite or overhaul core systems.
Southern Ohio Medical Center, for instance, used RealVNC to securely manage over 2,000 distributed endpoints across departments and reduce downtime.
4. Security challenges and data privacy
When you connect thousands of devices to the internet, you increase your attack surface. It’s that simple. Many connected medical devices were not designed with modern cybersecurity in mind.
Plus, patient data is some of the most sensitive information a system can store. That’s why regulations like HIPAA, GDPR, and EU MDR impose strict controls on how health data is transmitted, stored, and accessed. Any IoT healthcare solution must meet these standards or risk serious legal and reputational fallout.
This means access logs must be tamper-proof, sessions auditable, and permissions tightly controlled via role-based access control (RBAC).
Why RealVNC is a favorite among healthcare IoT solutions
RealVNC Connect helps healthcare IT teams:
- Enforce RBAC and session-based permissions
- Record and audit all session activity
- Deploy within air-gapped environments or DMZs
- Comply with standards like ISO 27001, HIPAA.
- Use end-to-end encryption for all data transmission
RealVNC Connect provides secure, auditable access to devices running major operating systems, like Windows and Linux.
It’s important to note that while RealVNC Connect offers broad device coverage (even to headless devices), it can’t support non-GUI interfaces. For these edge devices, an intermediary device would be needed, which RealVNC can be used to access remotely.
👉 This makes standardisation critical for interoperability, compliance, and scalable remote access you can monitor and trust.
RealVNC supports IoT in healthcare
RealVNC Connect isn’t an IoT device, but it is the secure bridge that helps healthcare IT teams manage the infrastructure surrounding those devices. Here’s how:
1. It supports secure access to IT systems
RealVNC Connect lets IT teams support systems across facilities, like in a workstation used by a clinician to view vitals or a backend server running scheduling software.
2. It supports the existing infrastructure
In scenarios where a nurse uses a tablet to check patient vitals hosted on a Windows machine, RealVNC facilitates secure access over the hospital’s network. No need to rebuild systems.
3. It supports maintenance and updates
With RealVNC, updates can be pushed remotely, without interrupting clinical workflows. It helps reduce downtime, increase IT responsiveness, and maintain patient care continuity, as seen in the Medical Board of California and Calderstones NHS Trust deployments.
Build a connected care system today

The most sophisticated IoT healthcare solutions mean little if the systems supporting them fail, stall, or get breached. This is why secure, auditable remote access matters.
If your hospital or clinic is planning to scale its IoT infrastructure, like through smart devices, virtual consults, or data integration platforms, make sure your support backbone is just as modern.
Explore RealVNC Connect today. It’s your healthcare-ready, standards-compliant remote access IoT healthcare solution.
FAQs
How does IoT improve patient care and operational efficiency?
IoT improves care and indirectly shapes patient health through remote, passive, continuous monitoring of vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, glucose levels, and oxygen saturation. This helps clinicians detect anomalies early and adjust treatment protocols fast. From an operational standpoint, IoT devices automate data collection, data storage, reduce manual inputs, and optimize resource allocation across healthcare systems.
What security challenges must healthcare providers address when implementing IoT?
Providers must ensure full compliance with HIPAA, GDPR, or other regional privacy frameworks and implement layered security strategies: role-based access control (RBAC), end-to-end encryption, audit logging, and network segmentation.
Why can RealVNC Connect only support devices with standard interfaces in the healthcare sector?
RealVNC Connect is engineered to provide secure, auditable remote access to devices running standard operating systems such as Windows or Linux. It relies on an interface layer to establish control, usually a GUI-based environment. Devices with proprietary or embedded-only firmware, such as headless monitors or hardware-locked IoT sensors, may lack the necessary interface to allow remote visualization or control.
How can healthcare organisations benefit from secure remote access solutions like RealVNC Connect?
Secure remote access allows IT teams to diagnose, configure, and update hospital systems, including EHRs, PACS servers, or nurse station desktops, all being physically present. Plus, RealVNC Connect supports encrypted, authenticated sessions with full session logging and RBAC, making it compliant with standards like HIPAA, ISO 27001, and EU MDR. In practice, this means hospitals can reduce mean time to repair (MTTR), ensure continuity of care, and maintain compliance without introducing operational risk.