What is remote access?
Essentially, remote access involves connecting to a computer or network in one location via a device in another location. Remote access allows users to retrieve files and use programs on another computer without seizing control of it – great for those who work from a distance and as a tool for online learning. This capability not only promotes seamless collaboration but also boosts productivity from virtually anywhere.
There are different applications for remote access that depend on the user’s role and needs. Remote desktop enables end users to operate a computer from afar as if they were sitting right in front of it. This functionality is particularly useful for comprehensive tasks that require full control over the remote system. On the other hand, screen sharing allows multiple users to view the same screen simultaneously, facilitating collaborative work and presentations.
Unattended remote access enables users to establish a remote control session on a device or desktop computer without requiring someone to be physically present at the remote device to authorize the remote connection. In contrast, remote control involves taking over control of another person’s computer from a remote device, and it is commonly used by IT support specialists to diagnose computer issues remotely.
How does remote access work?
A remote access connection can be achieved through several methods, the most common being virtual private networks (VPNs) and specialized remote access software. A VPN connects devices via a secure tunnel that ensures privacy and a smooth traffic flow. It encrypts data before sending it through the internet and decrypts it at the destination to maintain security.
Remote access software involves an ‘agent’ installed on devices like laptops and PCs, and a ‘platform’ deployed on the desired network. This setup bypasses the need for a VPN, as the platform directly recognizes the agent, facilitating a connection.
While different in application, both of these methods allow remote access and communication between devices.
For larger organizational needs, Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) tools are essential. They enable IT teams to manage thousands of remote devices efficiently, automating tasks such as software updates and policy enforcement, which reduces downtime and boosts productivity. This allows for large-scale management without the manual effort traditionally required, ensuring operations run smoothly and efficiently.
11 Types of remote access
The 11 ways that remote access is possible are via:
1. DSL (digital subscriber line)
DSL (digital subscriber line) utilizes a telephone network, DSL modem, and a high-speed internet connection. The DSL modem connects to the DSL network and uses existing phone lines to transmit digital data over the internet.
DSL enables faster and more reliable remote access than cellular internet, but it is not always an option without robust infrastructure.
2. Cable broadband
Possibly one of the most common remote access methods involves a cable modem and a high-speed internet connection. A VPN or RMM software is also required to connect to the target device or network securely.
Remote access is relatively fast and reliable with cable broadband, but it is limited to areas where cable infrastructure is available.
3. Cellular internet service
Remote access can be facilitated through cellular internet service, a cellular-enabled device, such as a smartphone or tablet, and a data plan. Cellular internet service works well to enable remote access but relies on a stable connection.
4. Satellite
Another connection method is via satellite with either a satellite modem, satellite antenna, or a VSAT (Very Small Aperture Terminal) system. The satellite modem is used to transmit data to and from the satellite, while the satellite antenna or VSAT system establishes a connection with the satellite.
5. Fiber optics broadband
Fiber optics broadband is one of the best remote access methods, especially for work that needs quick responses and minimal lag. It would help if you typically had a fiber optic modem, high-speed internet connection, and a VPN connection or remote desktop software.
Fiber optics broadband is not affected by electromagnetic interference or signal loss over long distances, unlike the copper cables used in DSL or cable broadband.
6. Virtual private network (VPN)
A VPN is a service that encrypts your internet connection to ensure private online activity and allows secure access to business networks from remote locations.
7. Local area network (LAN)
A LAN connection (local area network) is a network confined to a single location – such as an office, campus, or home.
8. Wide Area Network
A wide area network (WAN) is a network that spans multiple locations, such as different offices or branches of a company.
9. Desktop sharing
This method only works in tandem with another solution, as it requires an internet connection. You use remote desktop software and configure the host computer to allow remote desktop connections (RDC). From there, you can share your desktop. This is great for sharing presentations or for walking an IT team through a technical problem.
10. PAM (Privileged Access Management)
PAM is a security practice that helps organizations manage and secure privileged accounts that access sensitive systems and data. PAM provides secure access gateways that enable remote users to connect to privileged accounts, as well as allow you to specify individual access levels.
11. VPAM (Vendor Privileged Access Management)
VPAM is a security practice that enables organizations to manage and secure the privileged access of third-party vendors who need to access their systems remotely.
For this to be effective, it’s best to work with your IT team to identify the third-party vendors who require remote vendor access and restrict them to the areas they need.
What is a remote access protocol?
A remote access protocol is a set of rules that govern how a user or device can remotely access and communicate with a computer system or network.
These protocols define the methods of authentication and data transmission.
Remote access protocols typically use encryption and authentication mechanisms to ensure that remote access is secure and authenticated.
6 Types of remote access protocols
1. Serial Line Internet Protocol (SLIP)
SLIP is a protocol that operates at the OSI model’s data link and physical layers and generally offers low overhead costs.
It can transport TCP/IP over serial connections but lacks packet addressing and error-checking capabilities. SLIP can only be used on serial connections.
2. Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP)
PPP enables TCP/IP implementation through point-to-point links, dedicated leased lines, and dial-up connections. It is primarily used for remote connections to LANs and ISPs.
PPP leverages the Link Control Protocol (LCP) to establish communication between the PPP client and host.
PPP is associated with a high overhead cost and can be incompatible with older configurations.
3. Point-to-Point Tunnelling Protocol (PPTP)
Created by Microsoft, PPTP is a VPN protocol that enables secure communication between remote clients and private networks over the Internet.
PPTP also supports encryption and compression of the data being transmitted, providing enhanced security for communication.
4. Windows Remote Access Services (RAS)
RAS is a suite of features and protocols in Microsoft Windows operating systems that enable users to connect remotely to a network or computer from a different location over the internet or a private network.
RAS supports remote access technologies such as Virtual Private Network (VPN), Dial-up networking (DUN), and DirectAccess.
5. Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP)
Developed by Microsoft, RDP allows a user to remotely access and control another computer or virtual machine over a network connection. RDP is built into Windows operating systems and can connect to another Windows-based computer or a virtual machine running on a remote server.
6. Virtual Network Computing (VNC)
Similar to RDP, VNC allows users to control another computer remotely. However, in this case, a VNC server is installed on the remote computer (to be controlled), and a VNC viewer is installed on the device to control it from.
This offers greater flexibility, as it can be used across multiple devices and operating systems and has screen-sharing capabilities.
What are the benefits of remote access?
A secure remote access solution significantly enhances business operations across many sectors, offering both increased efficiency and improved security. Key benefits include:
Enhanced flexibility
Remote access allows employees to work from various locations at any time, boosting productivity by eliminating commutes and enabling a healthier work-life balance. This flexibility is crucial in a global business environment where teams are often spread across different time zones.
Cost reduction
Remote access supports a remote workforce, reducing or even eliminating costs associated with physical office spaces and commuting. Adopting a Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policy further reduces capital expenditure on hardware.
Improved security
Remote access enhances security by restricting physical and digital access to data and systems to authorized users only. This helps prevent data breaches and ensures data is secure, even off-site, protecting it against physical disasters.
Remote device management
Remote device management allows IT departments to centrally manage devices like workstations and mobile phones, ensuring compliance with the latest security policies and updates, thus securing the network.
IoT remote management
Expanding IT remote management to include IoT integrates complex networks of smart devices seamlessly into business operations. IoT remote management software offers tools for centralized diagnostics, firmware updates, and energy management. This is crucial for sectors like manufacturing and logistics, facilitating predictive maintenance, improving data analytics, and optimizing resource use for better efficiency and sustainability.
Adopting these technologies allows businesses to streamline IT management, swiftly adapt to changes, secure their operations, and sustain growth through enhanced scalability and flexibility.
How remote access improves remote work efficiency
A remote access solution streamlines remote work by enabling essential functions:
Efficient file transfer between local and remote desktops is critical. For example, a graphic designer can transfer large files from the company server to a home computer, ensuring access to the latest resources without needing to be at the office.
Remote printing allows employees to handle printing tasks from any location. A lawyer, for instance, can prepare for a court case by sending print jobs to the office printer from home, ensuring documents are ready upon arrival.
Remote viewing through desktop software facilitates administrative tasks and enhances team collaboration. It enables simultaneous access to the same computer by multiple users, crucial for projects with several stakeholders working remotely.
These functionalities reduce the need for physical office presence and allow continuous, efficient collaboration.
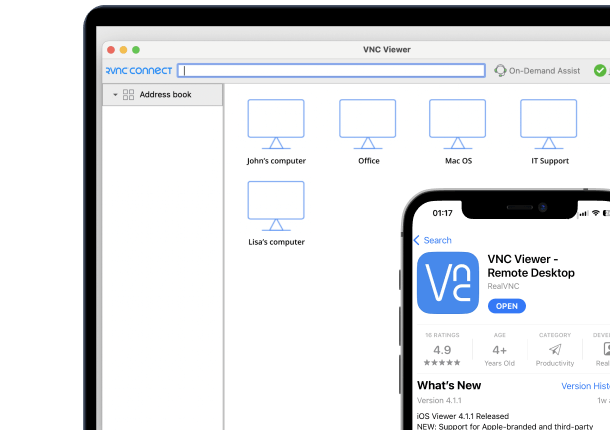
Enhance your organization’s efficiency with RealVNC’s remote access tool
RealVNC® takes your organization’s efficiency to the next level. RealVNC Connect allows a computer to be accessed and controlled remotely while the primary user can still interact with it. This makes it ideal for remote work purposes and training and support.
This sophisticated remote access technology, built with security in mind, allows your team to work from any location they choose – while using advanced administrative tools that provide you with complete control.
With your choice of connectivity options and enterprise-grade security, you can rest assured that RealVNC’s remote access tools are your solution to enhancing collaboration and productivity – across the board.